Which of the Mowing should be used to understand the context of testing within an organization?
You have assembled the following cost of quality numbers 1 000 defects were found prior to release and 100 were found after.
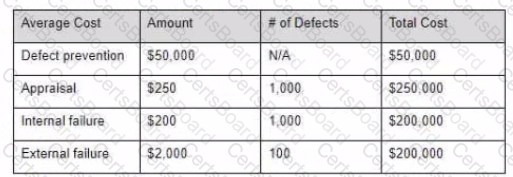
Given this information what should you conclude?
Your team has been assigned to test a loyalty card programfor a supermarket chain.Because this is a highly competitive market significant investment has been made to determine the shortcomings of the products offered by competitors While the feature sets are mostly the same, there is a wide variance In usability and performance and the users perceptions of these quality characteristics
Given only this information what test approach would be most appropriate?
Your defect opened trend is converging to the closed trend but there is still a gap. What does that gap represent?
Your team has been assigned to lest a new product thatis tightly integrated with existing systems The integrations include data transfers and transformations You have access to the architectural design documents and the integration specifications and some of your testers are former developers.
Given this information, what is the most appropriate test approach?
You have decided to help your team improve their skills. One of their assignments is to mentor a junior member of the team Which competency should you expect the mentor to develop during this exercise?
It the lest manager must repeatedly step in to resolve conflicts within the team what phase is the team in and what competencies arerequired from the test manager?
Your team has decided that they will build their own test management tool This will allow them to link the requirements and testcases together providing full traceability It will also allow them to create fully customized reporting and color-coded dashboards They have estimated the time required to create the new tool and the cost These fit within the project schedule and budget
What other consideration should be taken before this decision is made?
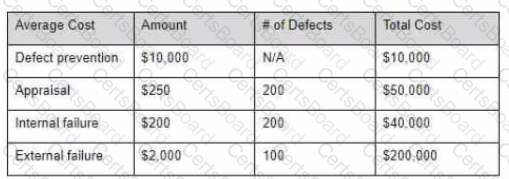
You have assembled the following cost of quality numbers 200 defects were found prior to release and 100 were found after.
Given this information what is the total cost of quality for this project?