Satish Dhawan, a veteran fixed income trader is conducting interviews for the post of a junior fixed income trader. He interviewed four candidates Adam, Balkrishnan, Catherine and Deepak and following are the answers to his questions.
Question 1: Tell something about Option Adjusted Spread
Adam: OAS is applicable only to bond which do not have any options attached to it. It is for the plain bonds.
Balkishna: In bonds with embedded options, AS reflects not only the credit risk but also reflects prepayment risk over and above the benchmark.Catherine: Sincespreads are calculated to know the level of credit risk in the bound, OAS is difference between in the Z spread and price of a call option for a callable bond.
Deepark: For callable bond OAS will be lower than Z Spread.
Question 2: This is a spread that must be added to the benchmark zero rate curve in a parallel shift so that the sum of the risky bond’s discounted cash flows equals its current market price. Which Spread I am talking about?
Adam: Z Spread
Balkrishna: Nominal Spread
Catherine: Option Adjusted Spread
Deepark: Asset Swap Spread
Question 3: What do you know about Interpolated spread and yield spread?
Adam: Yield spread is the difference between the YTM of a risky bond and the YTM of an on-the-run treasury benchmark bond whose maturity is closest, but not identical to that of risky bond. Interpolated spread is the spread between the YTM of risky bond and the YTM of same maturity treasury benchmark, which is interpolated from the two nearest on-the-run treasury securities.
Balkrishna: Interpolated spread is preferred to yield spread because the latter has the maturity mismatch, which leads to error if the yield curve is not flat and the benchmark security changes over time, leading to inconsistency.
Catherine: Interpolated spread takes account the shape of the benchmark yield curve and therefore better than yield spread.
Deepak: Both Interpolated Spread and Yield Spread rely on YTM which suffers from drawbacks and inconsistencies such as the assumption of flat yield curve and reinvestment at YTM itself.
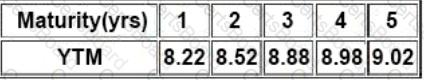
Then Satish gave following information related to the benchmark YTMs:
An investor decides to invest in the bond futures and has an outlook that the term structure curve would steepen. What should be his trading strategy?
Following is information related banks:
Auckland Ltd is a public sector bank operating with about 120 branches across India. The bank has been in business since 1971 and has about 40% branches in rural areas and about 75% of all branches are in
Western India. On the basis of the size, Auckland Ltd will be ranked at number 31 amongst 40 banks in India.
Although top management has appointment period of 5 years, generally they retire on ach sieving age of 60 years with an average tenure of only 2 years at the top job.
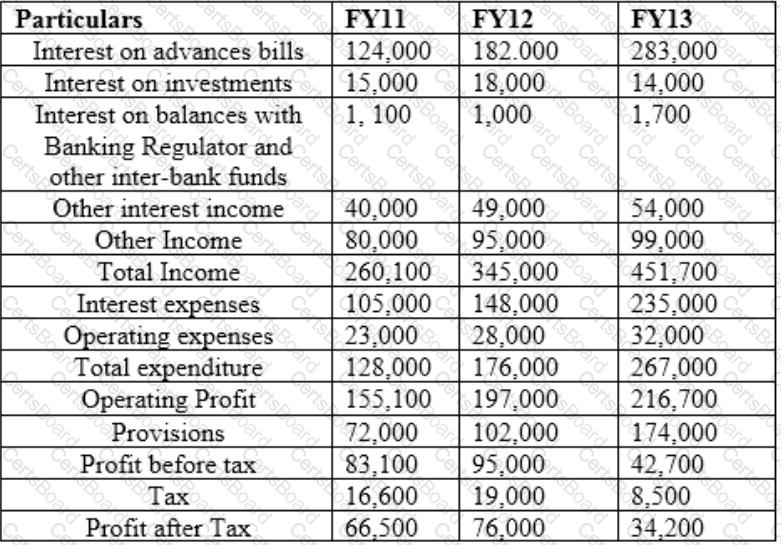
Profit and Loss Account
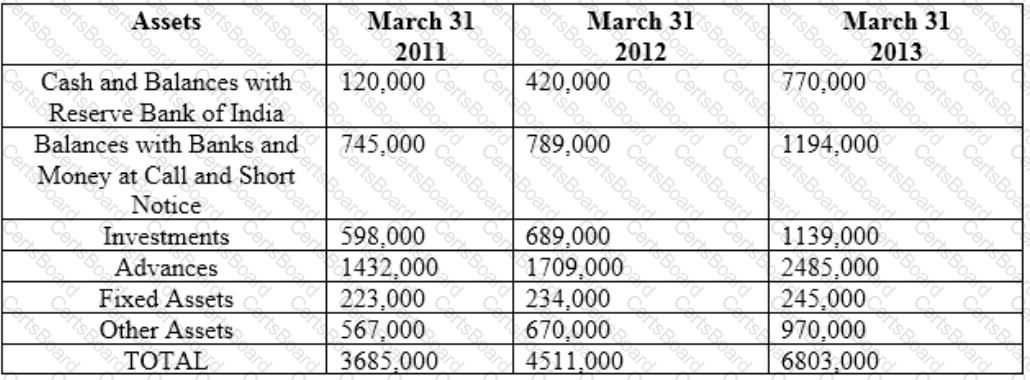
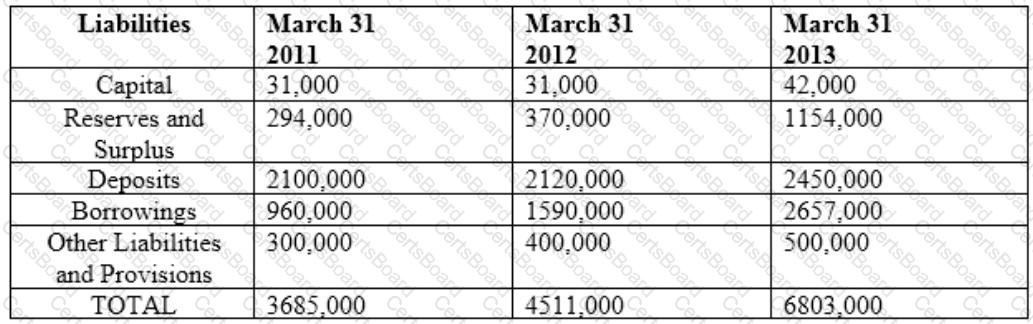
Balance Sheet
The rating wise break-up of assets for FY11 is as follows:
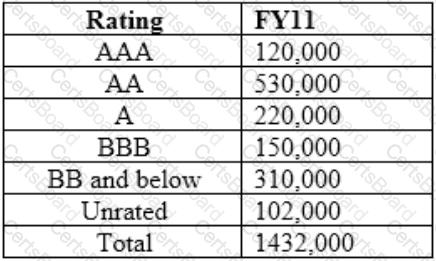
Cost to income ratio is best for which year
Satish Dhawan, a veteran fixed income trader is conducting interviews for the post of a junior fixed income trader. He interviewed four candidates Adam, Balkrishnan, Catherine and Deepak and following are the answers to his questions.
Question 1: Tell something about Option Adjusted Spread
Adam: OAS is applicable only to bond which do not have any options attached to it. It is for the plain bonds.
Balkishna: In bonds with embedded options, AS reflects not only the credit risk but also reflects prepayment risk over and above the benchmark.
Catherine: Sincespreads are calculated to know the level of credit risk in the bound, OAS is difference between in the Z spread and price of a call option for a callable bond.
Deepark: For callable bond OAS will be lower than Z Spread.
Question 2: This is a spread that must be added to the benchmark zero rate curve in a parallel shift so that the sum of the risky bond’s discounted cash flows equals its current market price. Which Spread I am talkingabout?
Adam: Z Spread
Balkrishna: Nominal Spread
Catherine: Option Adjusted Spread
Deepark: Asset Swap Spread
Question 3: What do you know about Interpolated spread and yield spread?
Adam: Yield spread is the difference between the YTM of a risky bond and the YTM of an on-the-run treasury benchmark bond whose maturity is closest, but not identical to that of risky bond. Interpolated spread is the spread between the YTM of risky bond and the YTM of same maturity treasury benchmark, which is interpolated from the two nearest on-the-run treasury securities.
Balkrishna: Interpolated spread is preferred to yield spread because the latter has the maturity mismatch, which leads to error if the yield curve is not flat and the benchmark security changes over time, leading to inconsistency.
Catherine: Interpolated spread takes account the shape of the benchmark yield curve and therefore better
than yield spread.
Deepak: Both Interpolated Spread and Yield Spread rely on YTM which suffers from drawbacks and inconsistencies such as the assumption of flat yield curve and reinvestment at YTM itself.
Then Satish gave following information related to the benchmark YTMs:
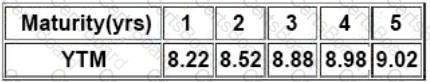
There is a 10.25% risky bond with a maturity of 4.75 year(s). Its current price is INR105.31, which corresponds
to YTM of 9.22%. Compute Interpolated Spread from the information provided in the vignette:
In Steepening short term rates ______relative to long term rate


