You are writing a postmortem for an incident that severely affected users. You want to prevent similar incidents in the future. Which two of the following sections should you include in the postmortem? (Choose two.)
You use Terraform to manage an application deployed to a Google Cloud environment The application runs on instances deployed by a managed instance group The Terraform code is deployed by using aCI/CD pipeline When you change the machine type on the instance template used by the managed instance group, the pipeline fails at the terraform apply stage with the following error message
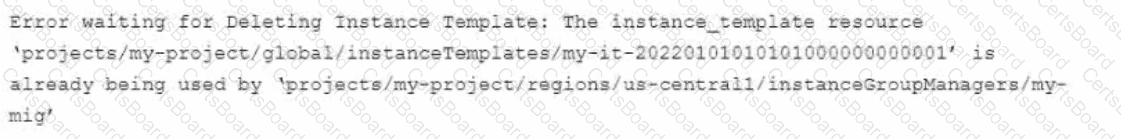
You need to update the instance template and minimize disruption to the application and the number of pipeline runs What should you do?
You are designing a new Google Cloud organization for a client. Your client is concerned with the risks associated with long-lived credentials created in Google Cloud. You need to design a solution to completely eliminate the risks associated with the use of JSON service account keys while minimizing operational overhead. What should you do?
Your team is preparing to launch a new API in Cloud Run. The API uses an OpenTelemetry agent to send distributed tracing data to Cloud Trace to monitor the time each request takes. The team has noticed inconsistent trace collection. You need to resolve the issue. What should you do?
You are configuring the frontend tier of an application deployed in Google Cloud The frontend tier is hosted in ngmx and deployed using a managed instance group with an Envoy-based external HTTP(S) load balancer in front The application is deployed entirely within the europe-west2 region: and only serves users based in the United Kingdom. You need to choose the most cost-effective network tier and load balancing configuration What should you use?
You are performing a semi-annual capacity planning exercise for your flagship service You expect a service user growth rate of 10% month-over-month for the next six months Your service is fully containerized and runs on a Google Kubemetes Engine (GKE) standard cluster across three zones with cluster autoscaling enabled You currently consume about 30% of your total deployed CPU capacity and you require resilience against the failure of a zone. You want to ensure that your users experience minimal negative impact as a result of this growth o' as a result of zone failure while you avoid unnecessary costs How should you prepare to handle the predicted growth?
Your product is currently deployed in three Google Cloud Platform (GCP) zones with your users divided between the zones. You can fail over from one zone to another, but it causes a 10-minute service disruption for the affected users. You typically experience a database failure once per quarter and can detect it within five minutes. You are cataloging the reliability risks of a new real-time chat feature for your product. You catalog the following information for each risk:
• Mean Time to Detect (MUD} in minutes
• Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) in minutes
• Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) in days
• User Impact Percentage
The chat feature requires a new database system that takes twice as long to successfully fail over between zones. You want to account for the risk of the new database failing in one zone. What would be the values for the risk of database failover with the new system?
You support a web application that runs on App Engine and uses CloudSQL and Cloud Storage for data storage. After a short spike in website traffic, you notice a big increase in latency for all user requests, increase in CPU use, and the number of processes running the application. Initial troubleshooting reveals:
After the initial spike in traffic, load levels returned to normal but users still experience high latency.
Requests for content from the CloudSQL database and images from Cloud Storage show the same high latency.
No changes were made to the website around the time the latency increased.
There is no increase in the number of errors to the users.
You expect another spike in website traffic in the coming days and want to make sure users don’t experience latency. What should you do?
You are developing a strategy for monitoring your Google Cloud Platform (GCP) projects in production using Stackdriver Workspaces. One of the requirements is to be able to quickly identify and react to production environment issues without false alerts from development and staging projects. You want to ensure that you adhere to the principle of least privilege when providing relevant team members with access to Stackdriver Workspaces. What should you do?
You are building and running client applications in Cloud Run and Cloud Functions Your client requires that all logs must be available for one year so that the client can import the logs into their logging service You must minimize required code changes What should you do?


