You have several different unstructured data sources, within your on-premises data center as well as in the cloud. The data is in various formats, such as Apache Parquet and CSV. You want to centralize this data in Cloud Storage. You need to set up an object sink for your data that allows you to use your own encryption keys. You want to use a GUI-based solution. What should you do?
You are deploying a new storage system for your mobile application, which is a media streaming service. You decide the best fit is Google Cloud Datastore. You have entities with multiple properties, some of which can take on multiple values. For example, in the entity ‘Movie’ the property ‘actors’ and the property ‘tags’ have multiple values but the property ‘date released’ does not. A typical query would ask for all movies with actor=

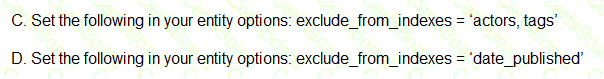
You have a query that filters a BigQuery table using a WHERE clause on timestamp and ID columns. By using bq query – -dry_run you learn that the query triggers a full scan of the table, even though the filter on timestamp and ID select a tiny fraction of the overall data. You want to reduce the amount of data scanned by BigQuery with minimal changes to existing SQL queries. What should you do?
You are designing a data mesh on Google Cloud with multiple distinct data engineering teams building data products. The typical data curation design pattern consists of landing files in Cloud Storage, transforming raw data in Cloud Storage and BigQuery datasets. and storing the final curated data product in BigQuery datasets You need to configure Dataplex to ensure that each team can access only the assets needed to build their data products. You also need to ensure that teams can easily share the curated data product. What should you do?
Your neural network model is taking days to train. You want to increase the training speed. What can you do?
You need ads data to serve Al models and historical data tor analytics longtail and outlier data points need to be identified You want to cleanse the data n near-reel time before running it through Al models What should you do?
You are building a streaming Dataflow pipeline that ingests noise level data from hundreds of sensors placed near construction sites across a city. The sensors measure noise level every ten seconds, and send that data to the pipeline when levels reach above 70 dBA. You need to detect the average noise level from a sensor when data is received for a duration of more than 30 minutes, but the window ends when no data has been received for 15 minutes What should you do?
You have 100 GB of data stored in a BigQuery table. This data is outdated and will only be accessed one or two times a year for analytics with SQL. For backup purposes, you want to store this data to be immutable for 3 years. You want to minimize storage costs. What should you do?
You launched a new gaming app almost three years ago. You have been uploading log files from the previous day to a separate Google BigQuery table with the table name format LOGS_yyyymmdd. You have been using table wildcard functions to generate daily and monthly reports for all time ranges. Recently, you discovered that some queries that cover long date ranges are exceeding the limit of 1,000 tables and failing. How can you resolve this issue?
You are building a teal-lime prediction engine that streams files, which may contain Pll (personal identifiable information) data, into Cloud Storage and eventually into BigQuery You want to ensure that the sensitive data is masked but still maintains referential Integrity, because names and emails are often used as join keys How should you use the Cloud Data Loss Prevention API (DLP API) to ensure that the Pll data is not accessible by unauthorized individuals?


